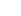dB, dBm ve dBi ile ilgili
Okumayı bitirmek için tahmini 15 dakika
DB (desibel)
DB, iki büyüklük arasındaki oranı temsil etmek için kullanılan göreceli bir birimdir. Genellikle güç veya voltajın (veya akımın) oranını tanımlamak için kullanılır.
Tanım: (dB=10 \ log_ {10} \ left (\ frac {P_2} {P_1} \ right)) veya (dB=20 \ log_ {10} \ left (\ frac {V_2} {V_1} \ right) )
Bunlardan (P_1) ve (P_2) iki güç değeri, (V_1) ve (V_2) ise iki gerilim veya akım değeridir.
Not: dB, mutlak bir değer değil, iki büyüklük arasındaki oranı temsil eden göreceli bir birimdir.
1. Güç oranı için desibel hesaplama formülü:
İki güç değerini karşılaştırırken desibel hesaplama formülü şöyledir:
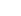
DB=10log10 (P1P2), burada (P_1) referans güçtür (genellikle sabit bir değerdir) ve (P_2) ölçülecek güçtür. (P_1) 1 watt ise yukarıdaki formül şu şekilde basitleştirilebilir: dB=10log10 (P2), burada (P_2) watt cinsinden güç değeridir.
2. Gerilim (veya akım) oranı için desibel hesaplama formülü:
İki voltaj (veya akım) değerini karşılaştırırken desibel hesaplama formülü şöyledir:
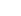
dB=20log10(V1V2)
belki
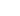
dB=20log10(I1I2)
Bunlar arasında (V_1) ve (I_1) referans gerilimleri ve akımlarıdır (genellikle sabit değerler), (V_2) ve (I_2) ise ölçülecek gerilim ve akımlardır. (V_1) veya (I_1) 1 volt veya 1 amper ise yukarıdaki formül şu şekilde basitleştirilebilir:
dB=20log10(V2)
belki
dB=20log10(I2)
Here (V_2) and (I_2) are voltage and current values in volts or amperes.
Note: In these formulas, (\ log_ {10}) represents the logarithm based on 10. If (P_2/P_1) or (V_2/V_1) (or (I_2/I_1)) is greater than 1, then the decibel value is positive; If it is less than 1, the decibel value is negative. The larger the decibel value, the greater the multiple of (P_2) relative to (P_1) (or (V_2) relative to (V_1), or (I_2) relative to (I_1)).

DBm (decibels milliwatts)
DBm is an absolute unit used to represent power values, with a reference point of 1 milliwatt (0.001 watt).
Definition: (dBm=10 \ log_ {10} \ left (\ frac {P} {1mW} \ right))
Where (P) is the power value to be measured.
For example, if the power of a signal is 1 watt, then its power is (10 \ log_ {10} (1000)=30 dBm).
DBm is commonly used to describe the power of wireless signals or the sensitivity of receivers.
DBm calculation formula
dBm=10log10(1mWP)
Among them,
(P) is the power value to be measured, in milliwatts (mW).
(1mW) is the reference power value, which corresponds to the power of 0dBm.
Related information
1. Unit conversion:
0dBm corresponds to 1 milliwatt (1mW).
For every 3dBm increase, the power doubles; For every reduction of 3dBm, the power is halved.
For example, 30dBm corresponds to 1 watt (1W), because (10 \ log_ {10} (1000)=30) (because 1W=1000mW).
2. Common conversion values:
o 30dBm = 1W
o 40dBm = 10W
o 50dBm = 100W
3. Precautions:
DBm represents the absolute value of power, not the power ratio.
In the calculation, pay attention to the unit of power and ensure that it is consistent with the unit of reference power (1mW).
Example
If the power of a signal is 4 watts (4W), then its power (in dBm) can be calculated as follows:
dBm=10log10(1mW4000mW)=10log10(4000)=10*(3+log10(4))≈36.02dBm
(Here (\ log_ {10} (4) \ approx 0.602) is the base 10 logarithm of 4)
DBi (decibels relative to isotropy)
DBi is a unit used to describe antenna gain, with its reference point being an idealized isotropic antenna (i.e. an antenna that uniformly radiates or receives in all directions).
Definition: (dBi=10 \ log_ {10} \ left (\ frac {G} {G_ {iso}} \ right))
Among them, (G) is the gain of the antenna to be measured, and (G_ {iso}) is the gain of an isotropic antenna (theoretically 1).
Note that since isotropic antennas do not exist in reality, dBi is a relative unit, but it provides a convenient reference point to compare the gains of different antennas.
DBi is commonly used to describe the gain of antennas used in wireless communication.
DBi calculation formula
dBi=10log10(E0E)
Among them:
(E) is the effective radiation power or gain of the actual antenna.
(E0) is the effective radiation power or gain of an ideal isotropic antenna. An ideal omnidirectional antenna has uniform radiation in all directions, and there is no such antenna in practice, so it serves as a reference benchmark.
Related information
1. Referans kriteri: dBi için referans kriteri, diğer antenlerin kazancını karşılaştırmak için kullanılan teorik olarak ideal bir model olan çok yönlü bir antendir.
2. dBd ile İlişki: dBi ve dBd'nin her ikisi de anten kazancını tanımlayan birimlerdir ancak referans standartları farklıdır. dBi için referans kriteri çok yönlü antendir, dBd için referans kriteri ise çift kutuplu antendir
(Dipol anten). Genellikle aynı kazancı temsil ederken dBi ile temsil edilen değerin dBd ile temsil edilen değerden 2,15 daha büyük olduğuna inanılır (yani dBi=dBd+2,15).
3. Örnek: Bir antenin kazancı dBd'de 16dBd olarak temsil ediliyorsa, o zaman kazancı dBi'de 18.15dBi olarak temsil edilir (genellikle ondalık basamaklar göz ardı edilirse 18dBi'dir).
Özetle dBi, anten kazancını tanımlamak için kullanılan bir birimdir ve hesaplama formülü, gerçek antenin etkin radyasyon gücünün ideal çok yönlü antenin etkin radyasyon gücüne oranına dayanmaktadır . DBd ile karşılaştırıldığında dBi'nin referansı çok yönlü antendir, dolayısıyla aynı kazancı temsil ederken dBi'nin değeri dBd'nin değerinden 2,15 daha büyük olacaktır.

















 MIMO Anteni
MIMO Anteni